Key Takeaways
- 6G telecom innovations will revolutionize wireless communications with ultra-fast speeds, AI-driven automation, and seamless global connectivity, enhancing industries like healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing.
- 6G networks will drastically reduce latency, enabling real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries, and next-generation immersive experiences like holographic communication.
- Telecommunication test equipment will evolve to support high-frequency ranges, real-time monitoring, and AI-powered diagnostics, ensuring 6G network reliability and efficiency.
- Challenges in 6G deployment include infrastructure costs, spectrum allocation, and cybersecurity risks, which must be addressed before widespread adoption around 2030.
- Sustainability in 6G will focus on energy-efficient technologies, green infrastructure, and minimizing electronic waste through advanced recycling methods.
The world of telecommunications is evolving rapidly. With 5G still rolling out across the globe, industry leaders are already looking ahead to 6G telecom innovations. The transition from 5G to 6G is expected to bring groundbreaking changes, from ultra-fast speeds to smarter networks powered by artificial intelligence. But what exactly does the future hold for 6G wireless communications? And how will telecommunication test equipment play a role in its development?
At Orbis Systems, we closely monitor these advancements to understand how they will impact the industry. This blog will break down the key innovations, challenges, and potential applications of 6G technology in a way that is easy for everyone to understand.
What is 6G Technology?
6G technology refers to the next generation of wireless networks, expected to launch commercially by 2030. While 5G has significantly improved data speeds and connectivity, 6G aims to take things even further. Experts predict that 6G networks will operate on higher frequency bands, possibly reaching the terahertz spectrum, allowing for near-instantaneous data transmission.
The main goal of 6G telecom innovations is to create a fully connected world where communication happens seamlessly. It is expected to revolutionize industries such as healthcare, transportation, and smart cities. This technology will not just be about faster smartphones but will also enhance automation, artificial intelligence, and digital interactions across various sectors.
How Fast Will 6G Be?
One of the most exciting aspects of 6G wireless communications is the potential for ultra-fast speeds. While 5G networks offer speeds of up to 10 Gbps, 6G is expected to be 100 times faster, reaching a peak of 1 Tbps. This level of speed will allow for real-time data sharing, reducing latency to nearly zero.
For example, in the medical field, surgeons could perform remote surgeries with complete precision, thanks to the instant transmission of high-resolution images and data. In the entertainment industry, users could download entire movies in seconds and experience truly immersive virtual reality without lag.
The Role of Telecommunication Test Equipment in 6G Development
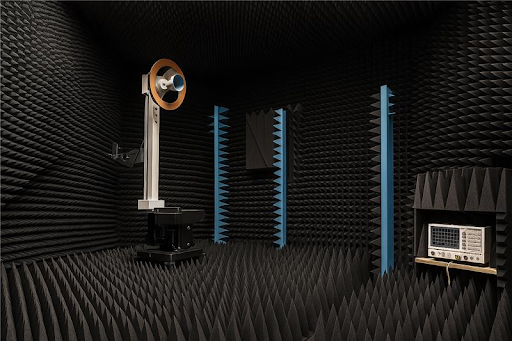
6G networks demand ultra-precise, high-frequency testing, far beyond what 5G required. Telecommunication test equipment plays a vital role in validating performance at terahertz frequencies, ensuring low-latency communication, and supporting advanced technologies like AI-driven automation and massive MIMO.
These systems simulate real-world conditions, measure beamforming accuracy, monitor signal integrity, and assess end-to-end latency. They’re also essential for testing cybersecurity protocols and network self-optimization features powered by AI.
As 6G evolves, reliable test solutions will be critical from R&D to deployment.
Key Innovations Driving 6G Networks
Several technological advancements will define the future of 6G networks. These include:
1. Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI will be at the core of 6G networks, allowing for smart optimization of network resources. Machine learning algorithms will predict data traffic patterns, improving efficiency and reducing congestion.
2. Terahertz Spectrum
Unlike 5G, which operates in the millimeter wave spectrum, 6G will explore even higher frequencies. This shift will enable significantly faster data transmission rates, but it will also require new infrastructure and telecommunication test equipment to handle the challenges of operating at such high frequencies.
3. Holographic Communication
Imagine having a video call where a 3D hologram of the other person appears in real-time. 6G is expected to make this possible by transmitting ultra-high-definition images instantly, providing a new level of communication.
4. Smart Surfaces and Reconfigurable Antennas
Smart surfaces and intelligent antennas will improve signal coverage, ensuring stronger and more reliable connections, even in dense urban areas. These advancements will help overcome obstacles like signal interference and limited range.
Challenges in Implementing 6G Networks
Despite its promising benefits, 6G technology faces several challenges before it can be widely adopted.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading existing networks to support 6G will require major investments.
- Energy Consumption: The higher speeds and increased data processing could lead to higher energy demands.
- Security Concerns: As data transmission speeds increase, so will the need for advanced cybersecurity measures.
- Standardization: Global cooperation will be necessary to establish universal standards for 6G networks.
6G Network Companies Leading the Way
Many global technology companies are already investing heavily in 6G research. These companies include major telecom providers, semiconductor manufacturers, and research institutions. Countries such as the United States, China, South Korea, and Japan are actively funding research into 6G wireless networks. Governments and private companies are working together to explore their potential, aiming to gain a competitive edge in the telecommunications industry.
The Future of 6G Wireless Communications
The evolution of wireless networks has always been driven by the need for faster, more reliable, and more efficient communication. 6G wireless communications will take connectivity to an entirely new level, supporting emerging technologies like quantum computing, edge computing, and extended reality.
With advancements in artificial intelligence and telecommunication test equipment, the future of 6G network companies looks bright. While the technology is still in its early stages, its potential to revolutionize industries and improve daily life is undeniable.
Conclusion
The evolution of wireless technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace, and 6G is set to redefine global communication. With groundbreaking innovations in AI, ultra-fast data transmission, and enhanced connectivity, the future promises seamless integration across industries. As research and development continue, 6G will unlock new possibilities, transforming how we interact with technology and each other. From smart cities to intelligent automation, the next generation of wireless networks will create a more efficient, connected, and sustainable world. The journey to 6G has just begun, and its impact will shape the future of communication for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is 6G technology?
6G technology is the next generation of wireless communication, offering ultra-fast speeds, near-zero latency, and AI-driven automation. It will enable seamless connectivity, support advanced applications like holographic communication, and transform industries by integrating AI, automation, and real-time data processing for a smarter, more efficient digital world.
2. When will 6G networks be available?
6G networks are expected to be commercially available by 2030. Research and development are already in progress, with companies and governments worldwide working on infrastructure, spectrum allocation, and technology standards. Early trials may begin by 2027, with widespread adoption following once key deployment challenges are addressed.
3. How will 6G impact daily life?
6G will revolutionize daily life by enhancing smart cities, healthcare, entertainment, and transportation. Expect real-time remote surgeries, AI-powered automation, immersive virtual experiences, and ultra-reliable autonomous vehicles. With faster speeds and smarter networks, 6G will create seamless digital interactions and drive advancements in global connectivity, making technology more efficient.
4. What role does AI play in 6G?
AI will optimize 6G networks by enabling self-healing, self-optimizing, and intelligent automation. It will predict network congestion, enhance security, and improve energy efficiency. AI-driven automation will ensure smooth communication between billions of connected devices, allowing real-time data processing, predictive maintenance, and enhanced cybersecurity for next-generation networks.
5. What are the challenges in developing 6G networks?
Developing 6G networks faces challenges like high infrastructure costs, spectrum allocation issues, cybersecurity risks, and technical complexities. Governments and companies must collaborate to create global standards, secure networks against cyber threats, and ensure sustainable, energy-efficient deployment while seamlessly managing the transition from 5G to 6G.